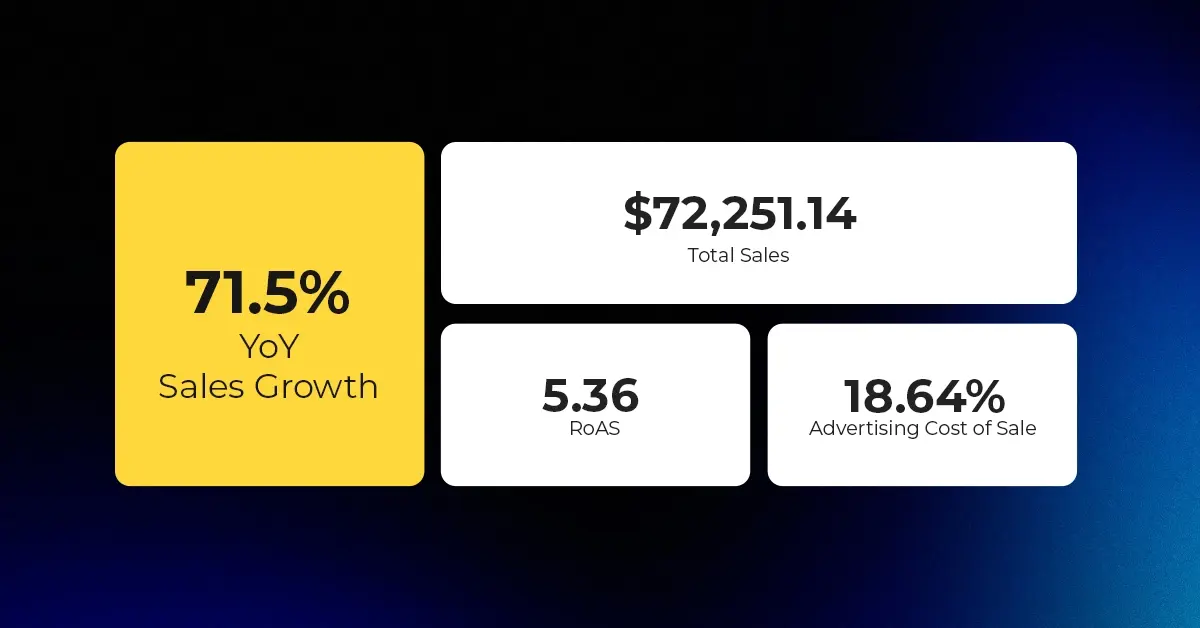
Major Developments
United States
A 100% tariff now applies to select Chinese-made port equipment and machinery, while new tariffs (25%–10%) on imported vehicles and auto parts target non-USMCA producers. A 90-day exemption window delays certain hikes until mid-November.
European Union
The EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) now exempts annual imports under 50 tons, easing compliance for small traders. However, the EU is also proposing stricter local-content requirements for batteries and energy tech — a signal for sellers to prepare for deeper localization demands.
China
New export licensing requirements for the entire rare-earth and battery-material supply chain introduce a “0.1% rule” — even minimal controlled content in products will need export clearance. This could affect electronics, EV parts, and semiconductor categories.
Shipping & Port Costs
Carriers including MSC, Maersk, and Hapag-Lloyd have introduced rate hikes and surcharges from Asia to Europe, Africa, and the Americas. European ports (Rotterdam, Antwerp) raised base tariffs while rewarding low-emission ships, signaling the industry’s green turn.
Implications for eCommerce Sellers
- Tighter Margins: Rising tariffs and freight surcharges mean higher landed costs. Expect thinner profit windows on imported electronics, auto accessories, and heavy goods.
- Sourcing Challenges: Export controls on Chinese inputs could slow shipments or force product redesigns for compliance. Sellers should diversify sourcing beyond high-risk regions.
- Compliance Complexity: Policies like CBAM and China’s dual-use licensing demand detailed reporting. Non-compliance could mean shipment delays or penalties.
- Shift Toward Localization: To bypass tariffs and controls, major marketplaces and sellers may expand local manufacturing or regional warehouses.
Next Steps for Sellers
- Audit supply chains to identify exposure to new tariffs, export bans, or port cost increases.
- Review pricing and margins with updated landed-cost models.
- Adopt compliance monitoring tools for real-time trade regulation updates.
- Diversify logistics routes — consider alternative ports and long-term carrier contracts.
- Stay proactive in communicating shipping or price changes to customers.
Bottom Line
November 2025 ushers in a tighter, greener, and more complex global trade era. For cross-border eCommerce sellers, success will hinge on operational agility, compliance discipline, and diversified logistics. Those who anticipate and adapt early will turn these policy shifts into a competitive advantage.
Related Reads
- Amazon Begins Quarterly Tax Reporting to China — What It Means for Cross-Border Sellers
- OpenAI and Amazon’s $38 Billion Cloud Deal: AI’s Next Big Leap for eCommerce
Source: CNABKE